Overview
To use the AKD, you must be able to communicate with the device using WorkBench and an Ethernet connection. The AKD uses TCP/IP. Both the AKD and the PC must connect through this standard in order to communicate.
Identifying the Drive IP Address
The first step in establishing communication with the device is to identify the device's IP address. WorkBench and the device find each other using this IP address. You can establish communication through the IP address with two types of connections:
- Automatic: Allow the device to automatically acquire an IP address.
- Direct: Connect to a device directly based on a known IP address.
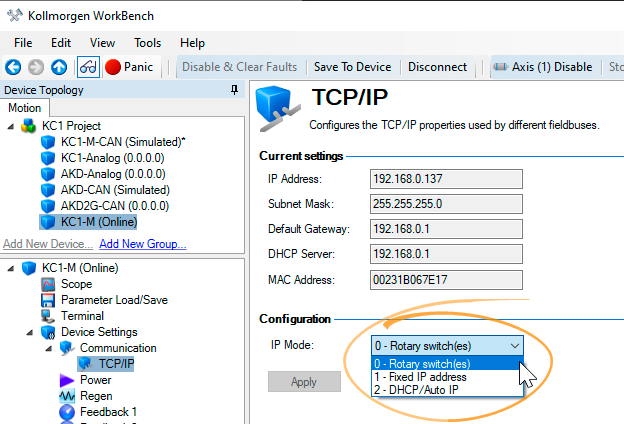
Select this connection type from the IP Mode drop-down box in the Communication View , or by setting IP.MODE from the terminal.
-
-
The current IP address can be found at any time by briefly pressing the B1 button. The address will flash sequentially on the front display.
Automatic (Dynamic) IP Addressing
Automatic (also called “dynamic”) addressing is performed using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). To put the device in DHCP mode, either:
- Set IP.MODE to 2
or
- Set IP.MODE to 0 and set the rotary switch(s) to 0.
The device will acquire its IP address from an external DHCP server if present in the network. If a DHCP server is not present, the device will assume an Automatic Private IP address of the form 169.254.x.x.
If your PC is directly connected to the device, and set to obtain an IP address automatically in the TCP/IP settings, a connection will be established with both devices using compatible automatically generated addresses. It can take up to 60 seconds for a PC to configure an Automatic Private IP Address (169.254.x.x).
When first communicating with the device, conflicts might exist with other programs or devices connected to your computer that are competing for IP addresses. If you have a problem recognizing a device, then try turning off other devices (especially a wireless device or remote network connection). If you still have problems connecting with the device, refer to Troubleshooting Connection and Communication Problems.
Static IP Addressing — Rotary Switches
Another option for connecting to the device is using a static IP connection. In this case a specific IP address is assigned to the device and the PC network configuration is modified to be able to recognize the static address. The device's IP address can be set using the rotary switch(s) on the front of the drive. IP.MODE must be set to 0.
-
-
When all of a device's rotary switches are set to 0, the device is in Automatic (Dynamic) IP addressing.
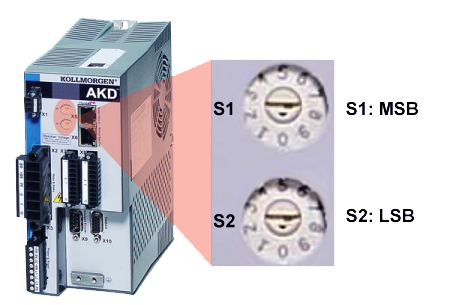
Devices with Two Rotary Switches
For drives with two rotary switches, the address will be set as 192.168.0.S1S2, with S1 representing the 10’s digit and S2 the 1’s digit. As you turn the switches, the drive displays the S1 and S2 values.
Example: S1 is set to 3, S2 is set to 5, the address now is set to: 192.168.0.35.
If the rotary switch is altered while 24 V Logic power is supplied to the AKD, you must turn the 24 V supply voltage off and then on again. This action will reset the address.
In order for the drive to connect to the PC, the PC network configuration must find this address. First, identify which network port you are using to communicate with the drive. Once you have identified the port, you can access the properties area of the network connection (on your PC) and set up the proper masking to allow the two devices to communicate. The configuration is set up in the “Use the following IP address:”. Set the IP address to 192.168.0.100 and the Subnet mask to 255.255.255.0. This allows the two devices to recognize each other and connect point to point (note that S1 = 0 and S2 = 0 is automatic (dynamic) IP adressing).
Devices with One Rotary Switch
Devices with one rotary switch do not support static IP addressing.
Static IP Addressing — Software Assigned
Full IP Addressing can be accomplished using four keywords accessible using terminal commands:
-
- Software assigned IP addressing is not available in AKD-C or AKD-N variants.
- IP.MODE: set Mode=1 to set a static IP address.
- IP.ADDRESS: specifies the address of the device.
- IP.SUBNET: specifies the subnet mask that the device can communicate with.
- IP.GATEWAY: specifies the gateway IP address if the device needs to communicate outside of its specified subnet.
Once the IP address has been properly configured using those four keywords, the IP.RESET command must be issued from the terminal. This will immediately implement the settings that have been configured. These settings must be saved to the device (DRV.NVSAVE) to remain in effect after power has been removed and restored.
Recovering communications with a device on an un-reachable IP address
Sometimes a device may be configured for an IP Address, and the device needs to be taken offline, and bench tested, or otherwise used outside of its saved IP Settings. If IP.MODE has been set to 1 (using software defined static IP) the device will boot up on an IP Address that may be unreachable with the host computer’s settings.
If the IP address prevents communication, the IP settings can be reset to default by the following procedure:
- Set the rotary switch(s) to 0
- Hold down button B1 (top-side of device) for 5 seconds.
The display will flash 0.0.0.0 and then attempt to discover an address by DHCP. Without removing logic power from the device, use WorkBench to connect to the device, reconfigure the IP address settings as desired, and store the values to non-volatile memory.
See Also
Rotary Switches | Communication View | Troubleshooting Connection and Communication Problems






